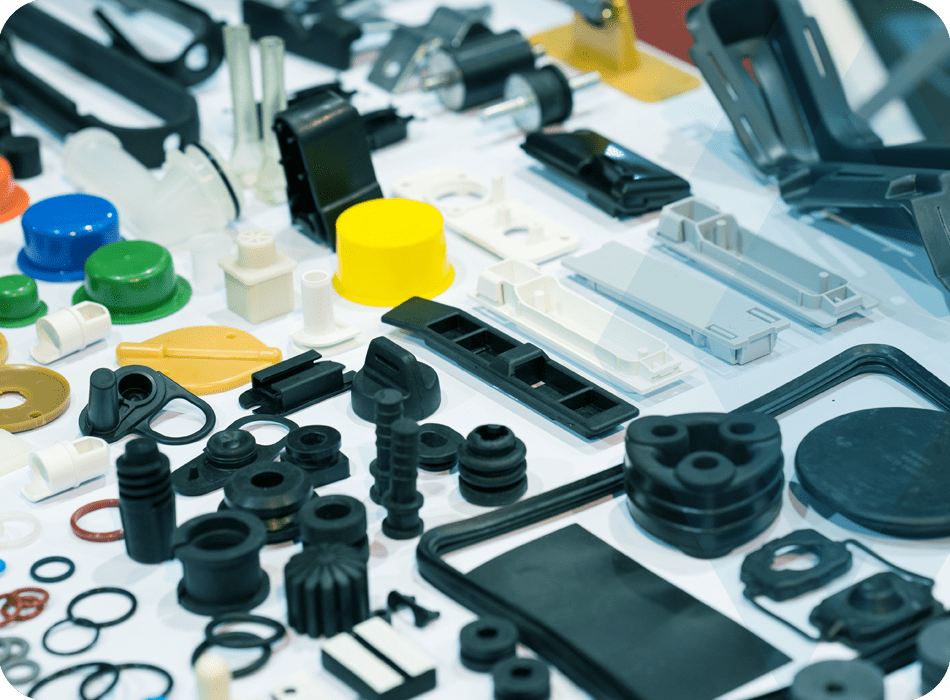
When it comes to manufacturing high-quality plastic components, choosing the best materials for injection moulding is one of the most important decisions you’ll make. The type of plastic selected affects everything from strength and flexibility to cost, finish, and environmental impact. At Flambeau Europe, we use a variety of performance plastics tailored to each application, and in this blog, we’ll walk you through some of the most common materials we work with, why they’re used, and how to pick the right one for your next project.

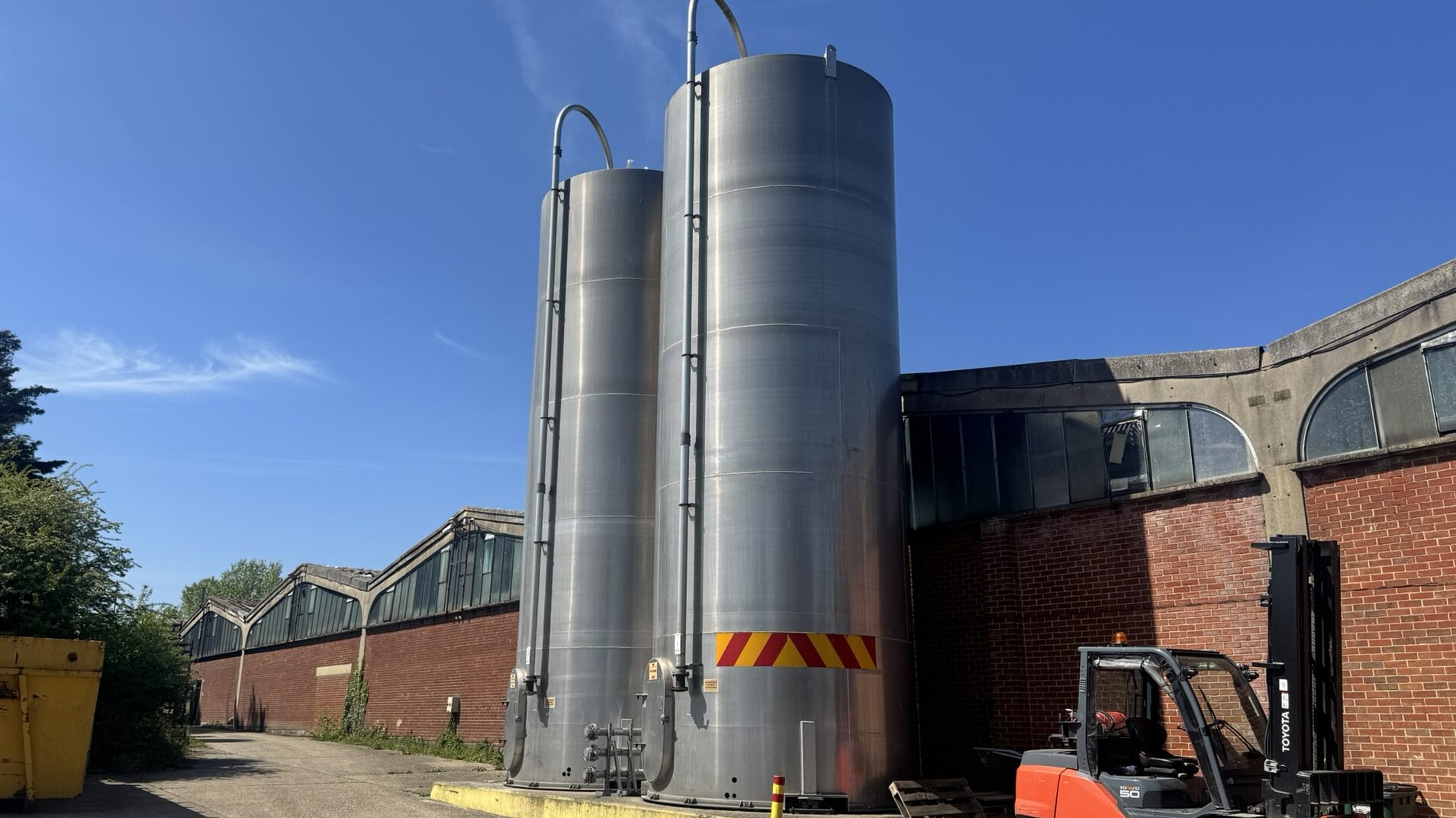
(Pictured, two of the silos Flambeau Europe use to house dozens of tonnes of plastic material)
Why Choosing the Best Materials for Injection Moulding Matters
The success of any injection moulded product starts with the right material. Choosing the wrong polymer can lead to issues in production, poor durability, or performance failure in the field. The best materials for injection moulding strike a balance between:
- Mechanical strength and flexibility
- Thermal and chemical resistance
- Surface finish and aesthetics
- Regulatory requirements (e.g. food or medical use)
- Cost and sustainability
From design feasibility to final application, material selection influences every stage of development, which is why it’s essential to understand your options.
1. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): A Strong, Versatile Material for Injection Moulding
Type: Thermoplastic polymer
ABS is a popular general-purpose plastic known for its excellent balance of toughness, strength, and visual appeal.
Features:
- High strength and rigidity
- Good impact resistance
- Excellent surface gloss and smoothness
Advantages:
- Easy to process and machine
- Electrically insulating
- Readily painted or glued
Disadvantages:
- Can deform under prolonged heat
- Limited UV resistance unless modified
Common Applications:
- Power tool housings
- Automotive dashboards
- Consumer electronics
- Toys (famously, LEGO bricks)

Sustainability:
ABS is recyclable and relatively durable. However, being a blended polymer, some recycling facilities may restrict it based on contamination. Long-life usage helps mitigate environmental concerns.
2. LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene): One of the Best Materials for Flexible Injection Moulded Products
Type: Thermoplastic polymer
LDPE is soft, flexible, and widely used in applications that demand pliability and moisture resistance.
Features:
- Excellent flexibility
- High impact and general chemical resistance
- Good transparency (in thin layers)
Advantages:
- Lightweight and economical
- Food-grade versions available
- Ideal for squeeze and snap-fit products
Disadvantages:
- Lower strength compared to other plastics
- Poor UV and temperature resistance
Common Applications:
- Lids and closures
- Flexible containers
- Squeeze bottles
- Medical tubing and packaging

Sustainability:
LDPE is recyclable (resin code #4), but is less commonly accepted curbside. Some bio-based alternatives are emerging to reduce fossil-based content.
3. Polypropylene (PP): Lightweight and Reliable Injection Moulding Plastic
Type: Semi-crystalline thermoplastic
Polypropylene is one of the most versatile and widely used materials in injection moulding, especially when lightweight and fatigue resistance are key.
Features:
- Good fatigue resistance
- Moisture and chemical resistance
- High melting point
Advantages:
- Ideal for living hinges
- Lightweight and strong
- Suitable for food, medical, and industrial uses
Disadvantages:
- Brittle at low temperatures
- Difficult to bond with adhesives
Common Applications:
- Reusable containers
- Hinged caps
- Automotive parts
- Home and garden items
Sustainability:
PP is fully recyclable and increasingly available in post-consumer recycled (PCR) versions. It also supports long-life use and reuse.
4. Polycarbonate (P): Tough, Transparent Plastic for Injection Moulding
Type: Amorphous thermoplastic
Polycarbonate is renowned for its incredible strength, transparency, and impact resistance, making it ideal for demanding applications.
Features:
- High clarity and toughness
- Flame retardant grades available
- Excellent dimensional stability
Advantages:
- Withstands impact better than glass or acrylic
- UV-stabilised options
- Heat-resistant
Disadvantages:
- Scratches easily unless coated
- More expensive than commodity plastics
Common Applications:
- Machine guards
- Safety eyewear
- LED housings
- Electronic enclosures

Sustainability:
Recyclable, though reuse is more common in industrial applications. High performance and long product life support sustainability goals.
5. Nylon (Polyamide, PA): Durable Engineering Plastic for Injection Moulded Components
Type: Engineering thermoplastic
Nylon is a strong, durable material widely used in functional components that endure mechanical stress.
Features:
- High mechanical strength
- Excellent wear and abrasion resistance
- Low coefficient of friction
Advantages:
- Ideal for gears and moving parts
- Good chemical resistance
- Heat-stable
Disadvantages:
- Absorbs moisture
- Requires drying before processing
Common Applications:
- Cable ties
- Bearings and bushings
- Automotive parts
- Tool handles

(Image credit: Travis Perkins)
Sustainability:
Nylon is partially recyclable, and newer bio-based variants (e.g. PA11 from castor oil) offer lower environmental impact. Its durability supports a long service life.
Sustainability and Plastic Material Selection
Material selection isn’t just about performance, it’s also about environmental responsibility. More customers than ever are seeking low-impact alternatives. At Flambeau Europe, we support this by:
- Using recycled content where possible
- Offering bio-based plastics for select applications
- Designing for product longevity and reuse
- Minimising waste through efficient tooling and regrind strategies
Whether you’re working toward ESG goals or simply want to make smarter material decisions, we’re here to advise on sustainable solutions. For more information, organisations like WRAP are working to help businesses reduce plastic waste and choose more sustainable materials.

(Image credit: Sun Chemical)
Making Plastic Do More: The Power of Masterbatch
Plastic is incredibly versatile, but it’s the masterbatch that unlocks its full potential.
By adding a masterbatch (a concentrated mix of additives or pigments) to the base resin, we can dramatically enhance the characteristics of the final product. That means we can:
- Match any colour to your brand palette
- Add UV protection for outdoor use
- Make parts antimicrobial for hygiene-sensitive settings
- Achieve medical-grade compliance
- Add fragrance for sensory appeal
- Make parts conductive or anti-static
- Improve fire retardancy for safety standards
- Even add glow-in-the-dark, metallic, or tactile effects
Whatever your needs, we can fine-tune the material to perform, protect, and stand out — while keeping costs efficient and manufacturing consistent.
👉 In the near future, we’ll be publishing a full deep dive into masterbatch, where we’ll explore the types available, how they work, and the many ways they can transform your injection moulded products. Stay tuned!
Final Thoughts: What’s Best for Your Product?
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to the best materials for injection moulding. The right choice depends on your specific product goals — from durability and aesthetics to compliance and environmental impact.
At Flambeau Europe, our team has decades of experience (view our history here) helping customers navigate the complexities of material selection. We don’t just manufacture — we collaborate, advise, and innovate. If you want to view and read more about our full capabilities as an injection moulding partner for you, read here.
💬 Ready to explore the best material for your next injection moulded product?
Contact us today to speak with our team — and discover how Flambeau can help bring your idea to life, with precision, performance, and a material that fits your vision perfectly.