3D printing in product development has become a transformative tool for designers, engineers, and manufacturers alike. By enabling rapid prototyping, iterative design, and cost-effective testing, 3D printing helps teams bring innovative products to market faster than ever before. At Flambeau Europe, we leverage 3D printing alongside traditional manufacturing methods, such as injection moulding, to ensure that our clients can explore designs fully before committing to full-scale production. Furthermore, this hybrid approach allows us to deliver high-quality components efficiently while reducing risk and costs.
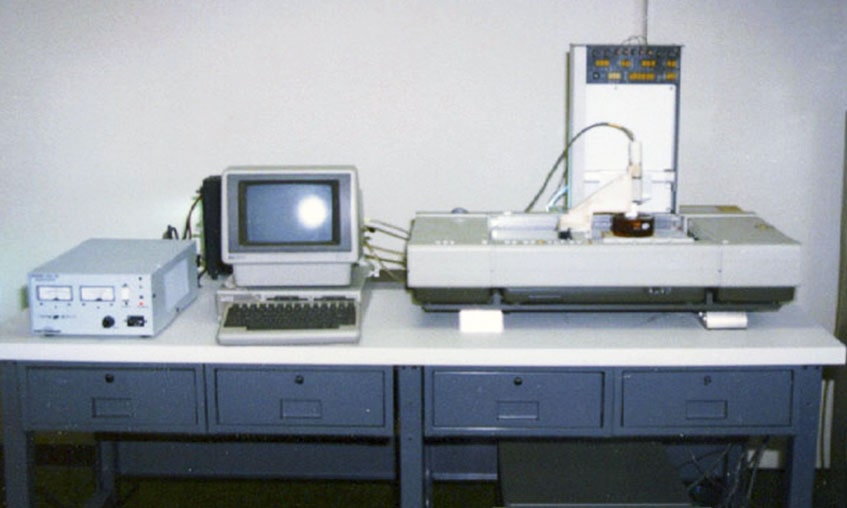

(First SLA-1 3D printer)
History of 3D Printing in Product Development
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has a fascinating history. The technology emerged in the 1980s, initially as a method for creating quick prototypes for product design. Over the decades, it evolved from a niche tool for industrial engineers into a widely adopted technique used across multiple industries, from automotive to healthcare. Early innovations were limited to basic thermoplastics, but today’s 3D printing technologies support advanced materials, functional prototypes, and even production-ready parts. Importantly, this evolution has laid the foundation for 3D printing to become an integral part of modern product development strategies.
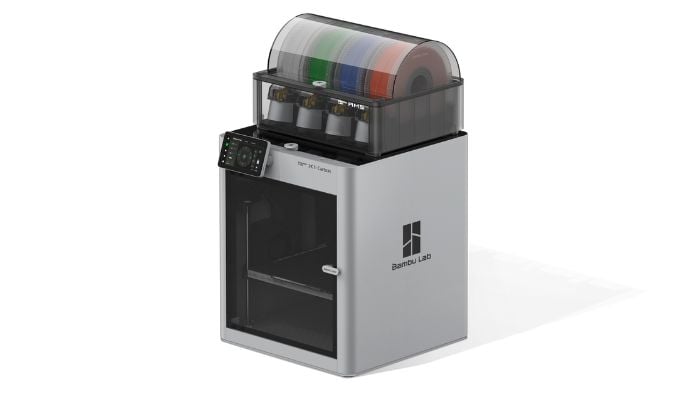

(2025 Bambu Labs 3D printer)
3D Printing Today: Modern Applications
In today’s product development landscape, 3D printing is no longer limited to simple prototypes. For instance, it enables:
- Rapid prototyping: Designers can quickly test form, fit, and function without investing in tooling.
- Functional testing: Early-stage products can undergo stress tests and quality assessments.
- Small-batch production: Limited runs of parts can be manufactured without costly setups.
Moreover, 3D printing allows teams to iterate on designs quickly, reducing time to market and improving overall efficiency. At Flambeau Europe, we have incorporated 3D printing into our workflow to support prototyping, tooling, and pre-production testing, ensuring that our injection moulding processes are as precise and efficient as possible.
Beyond traditional product development, 3D printing is now revolutionising industries far beyond plastics. Large-scale concrete printers are reshaping construction, with entire homes being printed layer by layer. In aerospace and automotive engineering, metal 3D printing enables the creation of complex, lightweight parts with remarkable strength. Even healthcare is benefiting, as surgeons and prosthetic designers use additive manufacturing for patient-specific implants and medical devices. These advances demonstrate how the technology continues to evolve and inspire innovation across sectors.
Learn more here: Top applications of 3D printing in manufacturing
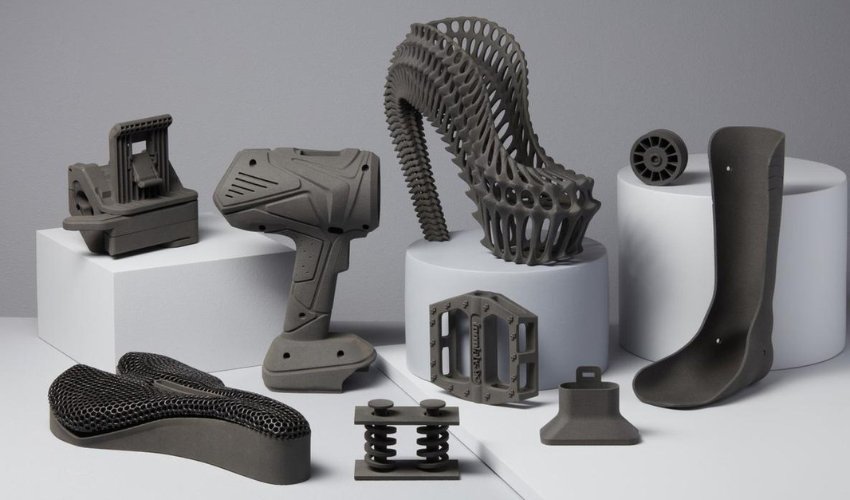

(Examples of 3D printed prototypes)
Integrating 3D Printing in Product Development with Injection Moulding
While 3D printing is ideal for prototyping and small batches, injection moulding remains the go-to solution for high-volume, consistent production. However, the two technologies are not mutually exclusive — in fact, they complement each other beautifully:
- Prototyping before tooling: 3D printing allows designers to validate parts before expensive tooling is created.
- Testing designs efficiently: Potential design issues can be identified and corrected early.
- Reducing lead times: By catching errors before full-scale production, overall project timelines are shortened.
At Flambeau Europe, this integration is also a cornerstone of our Complete Bespoke Solutions service. 3D printing sits alongside our full suite of capabilities—from consultation and design to tooling, moulding, finishing, and logistics. It enables us to deliver faster lead times and greater flexibility, ensuring each customer benefits from a truly end-to-end manufacturing experience. By combining these disciplines under one roof, we help our clients reduce risk, enhance collaboration, and achieve high-quality outcomes every time.
For more details on how we optimise injection moulding for complex components, see our guide on Optimising High-Precision Injection Moulding.
Benefits of Using 3D Printing in Product Development
There are several clear advantages to incorporating 3D printing into the product development process:
- Speed: Designers and engineers can iterate faster than traditional prototyping methods.
- Cost-efficiency: Reduces waste and eliminates the need for multiple costly tooling setups.
- Flexibility: Supports complex geometries and customised parts without extra expense.
- Collaboration: Enhanced communication between design, engineering, and manufacturing teams.
Additionally, visual aids such as 3D-printed models allow stakeholders to interact with prototypes, providing a tangible understanding of the product’s design and function. This ensures better alignment and reduces costly missteps later in production.
Furthermore, 3D printing enables teams to hold real, tangible prototypes, rather than relying solely on digital CAD models. Seeing and feeling a design in physical form provides invaluable insight into its proportions, usability, and finish, helping to bridge the gap between concept and final product far more effectively than a screen ever could.

(A future 3D printer designed for off-world production)
Future Trends in 3D Printing for Product Development
Looking ahead, 3D printing continues to evolve rapidly:
- Material innovation: New plastics, composites, and resins allow functional and durable parts.
- Hybrid manufacturing: Integration with CNC machining, robotics, and injection moulding enhances efficiency.
- On-demand production: Distributed and small-batch production models are becoming more viable.
- Sustainability: Reduced material waste and energy-efficient processes are gaining importance.
Looking forward, the next generation of 3D printing innovations is especially exciting. Researchers are developing multi-material and hybrid printing systems capable of producing flexible and rigid components in one continuous build. AI-assisted generative design is another major development, using machine learning to improve strength and reduce material usage automatically.
Meanwhile, biofabrication, the printing of organic tissue, is progressing rapidly, opening the door to medical breakthroughs such as artificial organs and biocompatible implants. Together, these technologies signal that the possibilities of 3D printing in product development are only just beginning to unfold.
For further insight into the future of manufacturing in the UK and emerging trends, see The Future of Plastic Manufacturing in the UK.
Conclusion
3D printing in product development has transformed how businesses design, prototype, and produce new products. By complementing injection moulding and other traditional manufacturing processes, it offers flexibility, speed, and cost-efficiency. At Flambeau Europe, we integrate 3D printing into our workflows to ensure that clients can explore every design possibility while reducing risk and accelerating time to market.
Ultimately, whether you are testing a new concept, validating a design, or preparing for full-scale production, 3D printing provides unmatched versatility and insight. Get in touch with our team today to explore how 3D printing and injection moulding can bring your product ideas to life.